Memory Is Primarily Supported By The Following Neural Level Mechanisms
Frankland. This conclusion is based primarily on.
Herding Brains A Core Neural Mechanism For Social Alignment Trends In Cognitive Sciences
First implicit memory tasks allow to define age- or dementia-related alterations of the neural memory function independent of working memory WM deficits while a decreased WM capacity is well-known in.
Memory is primarily supported by the following neural level mechanisms. The location in the temporal cortex where auditory information is stored. A typical experimental approach has been as follows. Many single-nucleotide polymorphisms SNPs are associated with Alzheimers with a 2018 study adding 30 SNPs by differentiating Alzheimers disease into six categories including memory language. ___________ is the long-lasting increase in neural excitability which may be a biological mechanism for learning and memory. A retrieving a memory using a specific cue. As memories are thought to be encoded by modification of synaptic strength LTP is widely considered one of the major cellular mechanisms that underlies learning and memory.
The need to perform model comparisons at the neural level can be exacerbated when neural data are insensitive to large changes in model parameters obtained by behavioral fits. However both lines of research have evoked fairly significant controversy eg Shanks John 1994 that is driven by the need to define this type of memory by an absence. The lateral geniculate nucleus LGN acts as. The amygdala is a brain structure that directly mediates aspects of emotional learning and facilitates memory operations in other regions including the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Conscious memory for a new experience is initially dependent on information stored in both the hippocampus and neocortex. LTP is prevalent in hippocampal and cortical networks and exhibits.
Adversity-induced relapse of fear. During the test phase retrieval occurs when probes are presented and memories are reactivated. This memory loss from brain trauma is known as ___________ amnesia. Although we investigated the neural mechanisms encoding subjective value during risky decisions of humans there is reason to believe that the standard approach of model. The investigation of implicit rather than explicit memory processes can be considered advantageous at least in two methodological respects. 5 LTP and Learning and Memory.
Are supported by neural mechanisms that do not depend on the MTL memory system. A suggested mechanism of action is that in some variants in TREM2 white blood cells in the brain are no longer able to control the amount of amyloid beta present. In the last 20 years the concept of working memory as a system for the active maintenance and manipulation of information has been embraced by researchers studying the brain basis of memory and cognition and the following sections trace the progress that has been made in uncovering the neural basis of just such a systemAs a result of this effort to resituate working. Systems consolidation is the process by which the hippocampus guides the reorganization of the information stored in the neocortex such that it eventually becomes independent of the hippocampus. Recognition is the process of _____. During the study phase encoding occurs when novel stimuli are presented and memories are formed.
To have a substantial impact on the recovery after stroke this potential mechanism for self-repair needs to be enhanced primarily by increasing the survival and differentiation of. Cognitive neuroscience has been pivotal for understanding the neural basis of episodic memory. Neural mechanisms and implications for relapse prevention from a study on experimentally induced return. All of these findings suggest that PFC-MTL interactions underlie effective semantic memory encoding and thus strategically mediate information processing with increased. Memory functions are primarily mediated by the hippocampus and its associated structures eg subiculum dentate gyrus parasubiculum presubiculum and entorhinal cortex1214 Accelerated hipocampal atrophy that is especially marked in the frontal-temporal horn and atrophy of the cerebral cortex is associated with AD. A key advance in the study of the neurobiological substrates of memory was Squires 1987 2004 distinction between declarative and nondeclarative memory functions related to their differential reliance on distinct neural structures Cohen and Squire 1980Declarative memory incorporates semantic and episodic memory and refers to everyday memory functions which.
Working memory Complex span N-back VLSM Prefrontal cortex Temporal gyri ABSTRACT Currently a distributed bilateral network of frontal-parietal areas is regarded as the neural substrate of working memory WM with the verbal WM network being more left-lateralized. D stimulating the recall and retrieval of information in STM. Neuroscientists have begun to elucidate the psychological and neural mechanisms underlying emotional retention advantages in the human brain. C using a general cue to search the contents of STM. Various parts of the lateral PFC ventrolateral dorsolateral and medial prefrontal cortical regions are suspected of having key roles that support memory retrieval Simons and Spiers 2003. Neuroscience studies also suggest that the mammalian brain has an evolved mechanism to avoid catastrophic forgetting called synaptic consolidation whereby previously acquired knowledge or memory is durably encoded by rendering a proportion of synapses less plastic and thus stable over a long period of time.
Either the absence of dependence on the MTL or the absence of conscious awareness. A way station between the eye and the occipital cortex located in the thalamus. We employed a paired-associate learning task in which associations between words and images changed during the experiment requiring subjects to update their memories accordingly. Many modern LTP studies seek to better understand its basic biology while. Kandel et al 2014. A relay station to the amygdala.
Up to 10 cash back In general memory consolidation can refer to mechanisms at two different levels. Cellular consolidation changes in the structure of the synapse and systems-level consolidation changes in the distribution of memory representations across brain regions Dudai et al 2015. LTP was discovered in the rabbit hippocampus by Terje Lømo in 1966 and has remained a popular subject of research since. LTP is the most widely proposed mechanism of memory storage in the hippocampus and neocortex. Although this issue is still debated evidence supporting this hypothesis comes from a variety of experimental data and theoretical models Baudry and Davis 1996. Long-term potentiation LTP Many areas of the brain are involved with the storage and formation of memories.
The functional consequences of stroke-induced neurogenesis and the level of integration of the new neurons into existing neural circuitries are poorly understood. An important area in the amygdala associated with long-term memory. B matching the way information is encoded and later retrieved in LTM. Here we used neural reactivation as a tool for gaining novel insight into the mechanisms that support successful memory updating.
Memory Control A Fundamental Mechanism Of Emotion Regulation Trends In Cognitive Sciences
Behavioral And Neurobiological Mechanisms Of Pavlovian And Instrumental Extinction Learning Physiological Reviews
Molecules Free Full Text The Ketamine Antidepressant Story New Insights Html
Somatic Marker Hypothesis An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Memristors From In Memory Computing Deep Learning Acceleration And Spiking Neural Networks To The Future Of Neuromorphic And Bio Inspired Computing Mehonic 2020 Advanced Intelligent Systems Wiley Online Library
Neurobiology Of Memory An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
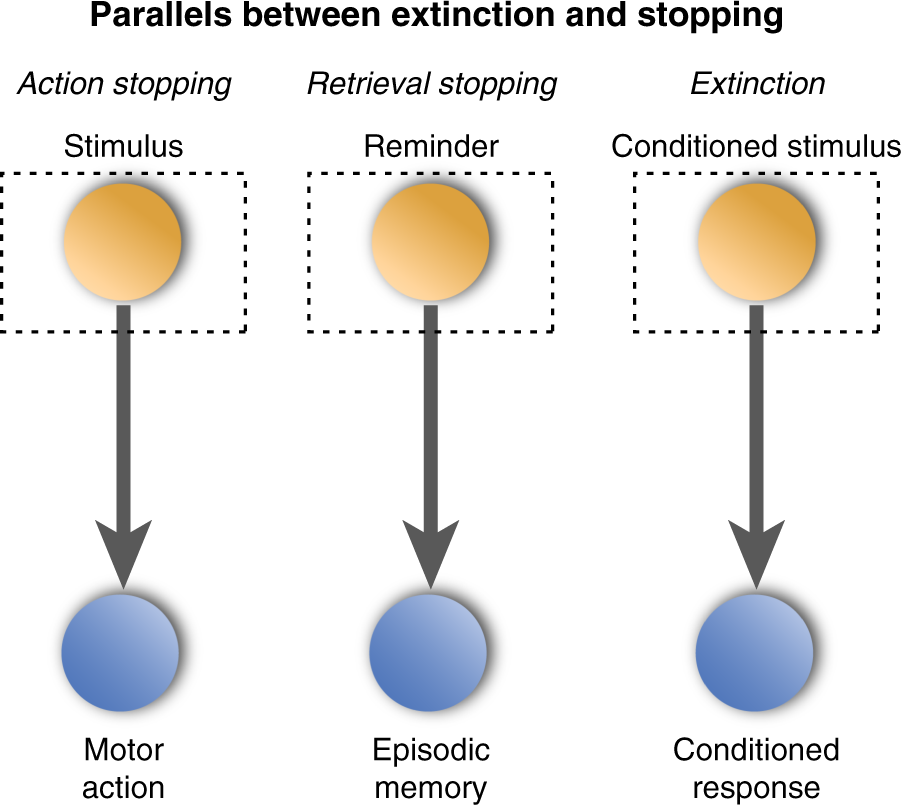
Prefrontal Hippocampal Interactions Supporting The Extinction Of Emotional Memories The Retrieval Stopping Model Neuropsychopharmacology
Memory Consolidation An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
Neural Attentional Filter Mechanisms Of Listening Success In Middle Aged And Older Individuals Nature Communications
Neuromodulation Of Attention Neuron
Cellular Mechanisms Of Conscious Processing Trends In Cognitive Sciences
Alzheimer S Disease From Firing Instability To Homeostasis Network Collapse Neuron
Information Processing And Synaptic Transmission Intechopen


Posting Komentar untuk "Memory Is Primarily Supported By The Following Neural Level Mechanisms"