Basal Ganglia Bleed Ppt
MEDS 371 01 Apr 10 323 DISEASES OF THE BASAL GANGLIA Hypokinesias impairment in initiation velocity and amplitude of movement hypertonia Hyperkinesias extra movements dyskinesias hypotonia Dementias. Blood supply Blood supply of the basal ganglia is provided via three arteries anterior choroidal middle cerebral and anterior cerebral.
Axial SWI shows a large hypertensive basal ganglia hemorrhage as well as multiple foci of susceptibility artifact.
Basal ganglia bleed ppt. Hypertensive-type Intracerebral Hemorrhage Basal ganglia 60 Thalamus 20 Pons cerebellar 10 Review NEJM 2001. Sixty percent of hypertensive intracerebral hemorrhage is located in the basal ganglia. Acute IPH is identified by head CT as an intra-axial hyperdense region of hemorrhage that is classically centered within the basal ganglia cerebellum or occipital lobes Figure 7. This results in oligaemia neuro-transmitter release mitochondrial dysfunction and cellular swelling. The basal ganglia play a major role in. Hemorrhage left basal ganglia 32 x 15 cms ruptured into left lateral ventricle small amount of blood in right lateral ventricle and 3rd ventricle 26 case study.
Usually as a result of poorly controlled long standing hypertension and the stigmata of chronic hypertensive encephalopathy are often present. The area of the basal ganglia is the part of the brain most frequently affected by haemorrhages. Intraparenchymal hemorrhage IPH secondary to hypertension typically affects patients in their sixth and seventh decades of life and has a 30-50 mortality rate. Causes symptoms treatment and diagnosis - Basal ganglia disease refers to a group of physical dysfunctions that occur when the group of nuclei in the brain known as the basal ganglia fail to properly initiate movements. Basal ganglia Corpus striatum The basal ganglia or basal nuclei are a group of subcortical structures found deep within the white matter of the brainThey form a part of the extrapyramidal motor system and work in tandem with the pyramidal and limbic systems. Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathy Amyloid-beta deposition in leptomeningeal and cortical arteries arterioles veins and capillaries Sporadic but associated with ApoE ε4 and ε2 alleles.
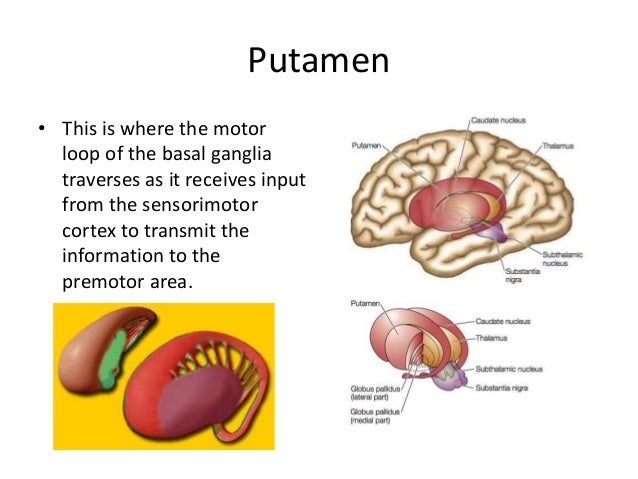
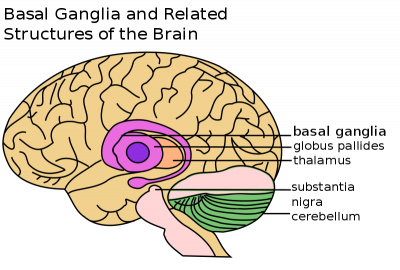
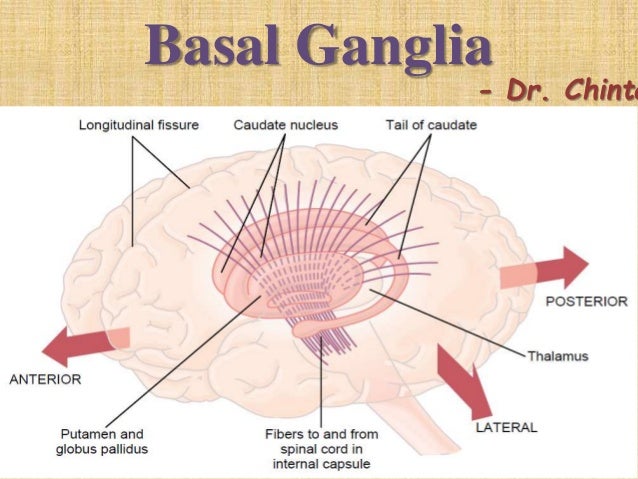
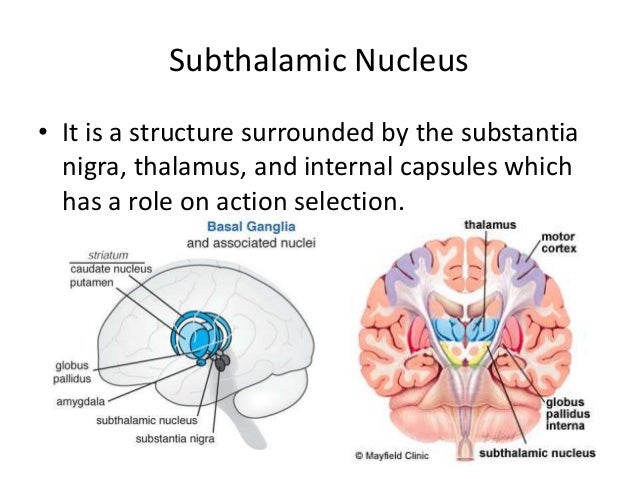
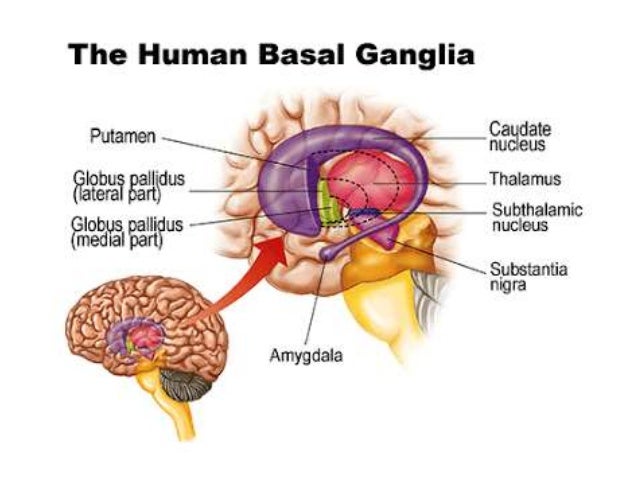
Caudate nucleus putamen globus pallidus. PowerPoint PPT presentation free to view. The commonest etiology for such bleeds is small vessel vasculopathy secondary to chronic long-term hypertension. The basal ganglia refers to a group of subcortical nuclei responsible primarily for motor control as well as other roles such as motor learning executive functions and behaviors and emotions. This in conjunction with increased pressure from within the lumen causes vascular rupture and hemorrhage. Connection of basal ganglia.
Physiology of Basal Ganglia. Basal ganglia or thalamic location Criteria for Diagnosis. 1 ruptured vascular malformations aneurysms - second most common cause of ICH. 45 yo man with confusion lethargy since yesterday 293. The hematoma disrupts the neurons and glia. Basal Ganglia ------ Group of nuclei mass of grey matter in the forebrain and upper part of the brain stem that have motor function of great importance -- Head ganglia of Motor control.
Basal ganglion lesions in Psychiatric Diseases ADHD. A brain haemorrhage causes blood to accumulate inside the brain. Ich-labs wbc 431 hgb 124 hct 357 plat 198 inr 21 aptt 35 glu 109 bun 11 cr 96 na 141 k 33 cl 119 co2 17 ca 83 alb 21 alt 40 ast 38 alkphos 92 t bili 02 25 26. The basal ganglia consist of five pairs of nuclei. Basal Ganglia Stroke Muhammad Asim Rana MBBS MRCP EDIC SF-CCM FRCPE. Although the etiology of ADHD yet has to be determined there is a growing consensus that the condition involves functional and anatomical dysfunction in the brains frontal cortex and basal ganglia segments of the cortico-basal ganglia-thalamo-cortical circuitry.
Cerebral Cortex Basal Ganglia SJCSJP. Learn how to recognize its specific symptoms as well as the general symptoms of stroke. Basal ganglia disease. Friday March 4 2016. Hypertensive Hemorrhage Common Locations Basal ganglia Thalamus Brain stem Cerebellum Cerebral hemisphere 50 5 10 10 25. Hypertensive hemorrhage is parenchymal and its most frequent sites of are the basal ganglia and thalamus.
Proposed more than two decades ago the classical basal ganglia model shows how information flows through the basal ganglia back to the cortex. Basal ganglial haemorrhage A basal ganglial haemorrhage is a common form of intracerebral haemorrhage. Other sites of hypertensive haemorrhages are the pons and the cerebellum. Basal ganglia haemorrhage bleeding A basal ganglia haemorrhage is bleeding from blood vessels in an area of the brain that responsible for body movements sensation speech and personality. Less commonly it involves the cerebellum the pons and occasionally the subcortical white matter. A basal ganglia stroke affects the part of the brain that controls movement perception and judgment.
Striatal Synaptic Plasticity Regulates Circuitry Striatum is the major input nucleus to the basal ganglia Striatal MSNs exhibit very negative resting potentials -85 mV due to high Kir expression Striatal MSNs require coordinated presynaptic excitatory activity in order to depolarize sufficiently to fire action. Many observational and epidemiological studies have identified a wide range of factors that are predictive of outcome after evacuation of hematoma including. Young normotensive patients with lobar and. Axial CT in a 61-year-old hypertensive woman shows the classic appearance of a left basal ganglia hemorrhage involving the putamen and external capsule striatocapsular. They are significantly united with the cerebral cortex thalamus and brainstem. Note areas of periventricular hypodensity likely related to chronic small vessel ischemia.
What are Basal Ganglia The basal ganglia or basal nuclei are group of subcortical nuclei located at the base of the forebrain. The caudate nucleus with its extended gray mass is C-shaped with a head that is continual with the putamen a body and a tail. Structural lesions most common etiology in lobar hemorrhages vs. Only rarely affect basal ganglia thalamus pons Child with ICH AVM until proven otherwise. The common sites of the bleed are the basal ganglia 50 cerebral lobes 10 to 20 the thalamus 15 pons and the brain stem 10 to 20 and the cerebellum10fig123. INTRACEREBRAL HEMORRHAGE ICH Vas20 3 3.
MEDS 371 29 Mar 12 223 How Did Disease Help Elucidate the Functions of the Basal Ganglia.

Basal Ganglia Direct And Indirect Pathway Of Movement Osmosis

Reticular Formation The Reticular Formation Extends Through The Central Core Of The Medulla O Reticular Formation Brain Anatomy And Function Brain Anatomy

Stroke Basal Ganglia Bleed Basal Ganglia Brain Facts Human Anatomy And Physiology
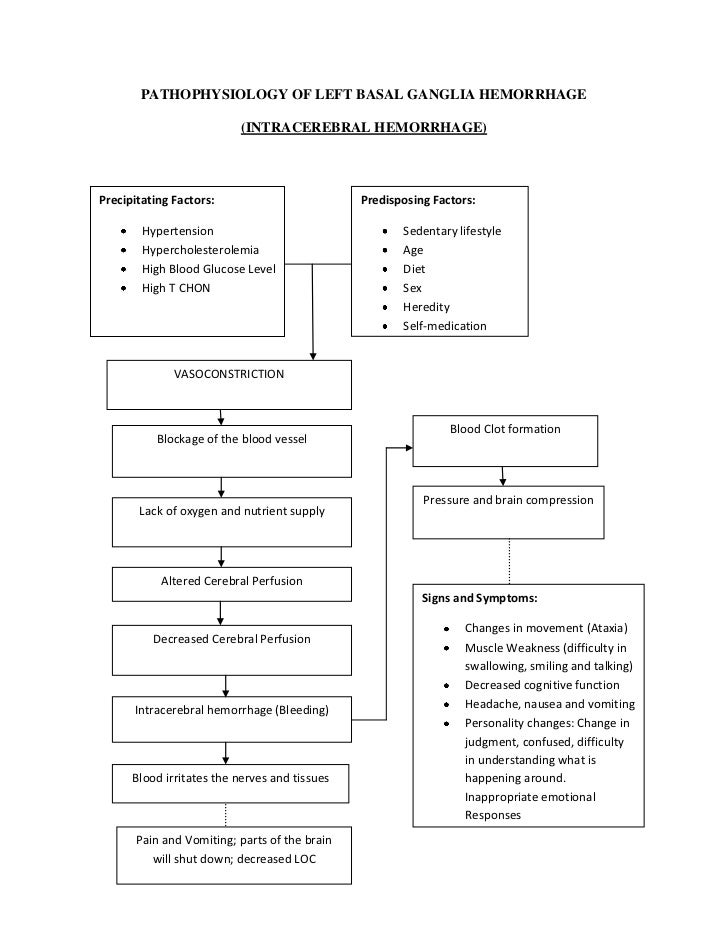
Pathophysiology Of Left Basal Ganglia Hemorrhage






Posting Komentar untuk "Basal Ganglia Bleed Ppt"